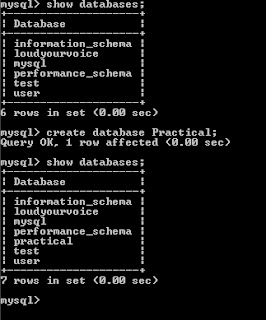
1. a) Create
your own database.
create database Practical;
b) Create table
within it with the following fields giving name as Employee
table. (Empno, empname, Job, Salary, Deptno.)
create table Practical.Employee(
Empno int(5),
Empname varchar(50),
Job varchar(50),
Salary float(10,2),
Deptno int(3)
);
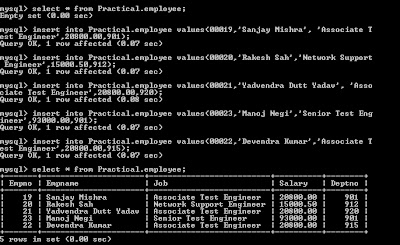
c) Insert five
records in above created table.
insert into Practical.employee
values(00019,'Sanjay Mishra', 'Associate Test Engineer',20800.00,901);
insert into Practical.employee values(00020,'Rakesh
Sah','Network Support Engineer',15000.50,912);
insert into Practical.employee values(00021,'Yadvendra
Dutt Yadav', 'Associate Test Engineer',20800.00,920);
insert into Practical.employee values(00023,'Manoj Negi','Senior
Test Engineer',93000.00,901);
insert into Practical.employee
values(00022,'Devendra Kumar','Associate Test Engineer',20800.00,915);
d) Verify by displaying data by select statement.
Select * from
Practical.employee;
2. Use Employee table :
a) Display
records of a selected deptno.
Select * from
Practical.employee where Deptno=901;
b) Display the
record of selected person.
Select * from Practical.employee where Empname=’Sanjay
Mishra’;
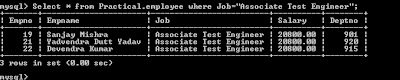
c) Display the
record of selected Job.
Select * from Practical.employee where Job=”Associate
Test Engineer”;
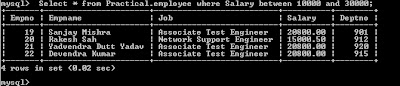
d) Display the records of given selected salary range.
Select * from Practical.employee where Salary between
10000 and 30000;
e) Display only
the selected columns.
Select Empname, Job
from Practical.employee;
f) Display by
adding some title to the column.
Select Empname AS “List of Employee” from
Practical.employee;
3. Use Employee table :
a) Add
one more column to table i.e. Phone_no.
b) Modify the Employee name
column by changing the data length
c) Make the empno.
as primary key.
d) Insert data in phone field of each each employee by selecting
him with empno.
UPDATE
Practical.employee SET Phone_no=”9910358271” WHERE Empno=019;
UPDATE
Practical.employee SET Phone_no=’7875277745’ WHERE Empno=020;
UPDATE
Practical.employee SET Phone_no=’9560731770’ WHERE Empno=021;
UPDATE
Practical.employee SET Phone_no=’9650022039’ WHERE Empno=022;
4. a) Create another table dept with three
column:
deptno,
dname and Location with deptno was primary key.
CREATE
Table Practical.dept(
Deptno int(3) Primary Key,
Dname varchar(50),
Location varchar(30)
);
Insert
records in it keeping in view deptno in employee table.
INSERT INTO Practical.dept
VALUES(901,’ Computer’,’Gurgaon’);
INSERT INTO Practical.dept VALUES(912,’HR’,’Nagpur’);
INSERT INTO Practical.dept VALUES(920,’Sales’,’Gurgaon’);
INSERT INTO Practical.dept VALUES(915,’Finance’,’Gurgaon’);
b) Create the relation between employee table and Dept table on the basis of deptno that mean
deptno in the employee will be as foreign key in that table.
ALTER Table
Practical.employee ADD FOREIGN KEY(Deptno) REFERENCES Practical.dept(Deptno);
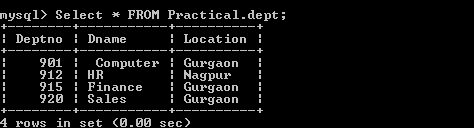
c) Display the available records in dept table.
Select *
FROM Practical.dept;
5. a) Insert
some more record in employee table and verify the effects of
constraints
applied in adding deptno.
insert into Practical.employee values(00025,'Ravi Jain', 'Manager',30000.00,913,9911004410);
insert into Practical.employee values(00026,'Saina soni', 'Technical
Leader',25000.00,913,9911345510);
Unable to insert into
employee table until we add deptno into dept table
INSERT INTO Practical.dept
VALUES(913,’Marketing’,’Delhi’);
b) Update records
of some employee by transferring them from one dept to
another.
UPDATE Practical.employee
SET Deptno=913 WHERE Empno=23;
UPDATE Practical.employee
SET Deptno=912 WHERE Empno=26;
c) Update the salary of some employees (give 10% increase)
on dept basis
in employee table.
UPDATE Practical.employee
SET Salary=(Salary+10/100*Salary) WHERE Deptno=912;
d) Delete some
record from employee table and verify
the output using select.
DELETE From Practical.employee WHERE Empno=26;
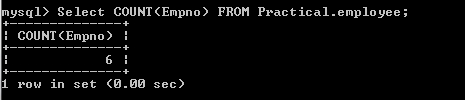
6. a) Count
the total no of employee.
Select
COUNT(Empno) FROM Practical.employee;
b) Count
the sum of salary using employee table.
Select
SUM(Salary) FROM Practical.employee;
c) Calculate
the avg salary of employee.
Select
AVG(Salary) FROM Practical.employee;
d) Determine
the max and min salary of employees.
Select
MAX(Salary) FROM Practical.employee;
Select
MIN(Salary) FROM Practical.employee;
7. a) Count
the no of employees deptt wise using Group by & having clauses.
Select
Deptno, Count(Deptno) FROM Practical.employee group by Deptno Having
Count(Deptno)>0;
b) Display
the some of salaries deptt wise.
Select
Deptno, SUM(Salary) FROM Practical.employee group by Deptno;
c) Display
avg salary deptt wise.
Select
Deptno, AVG(Salary) FROM Practical.employee group by Deptno;
d) Display
max and min salary deptt. wise.
Select
Deptno, MAX(Salary) FROM Practical.employee group by Deptno;
Select
Deptno, MIN(Salary) FROM Practical.employee group by Deptno;
8. a) Display
emp_no and emp name from employee table alongwith deptt. name from
dept table.
Select
Empno, Empname, Dname FROM Practical.employee, Practical.dept WHERE
employee.Deptno= dept.Deptno;
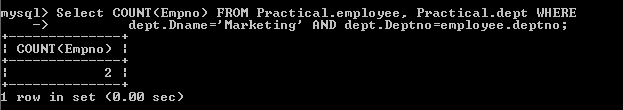
b) Count employee of employee table by giving department name.
Select
COUNT(Empno) FROM Practical.employee, Practical.dept WHERE
dept.Dname=’Marketing’
AND dept.Deptno=employee.deptno;
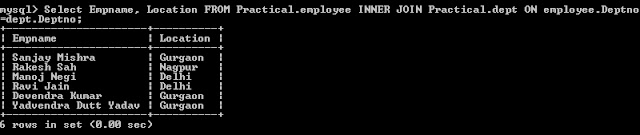
c) Display
some more lists by using join statement.
Select
Empname, Location FROM Practical.employee INNER JOIN Practical.dept ON
employee.Deptno=dept.Deptno;
9. a) Create
table by using sub query statement. Display the records.
CREATE
table Practical.temp as Select * FROM Practical.employee;
Select
* FROM Practical.temp;
b) Create table with selected column by using sub queries.
Display the output
to see data.
CREATE
table Practical.branch as Select DISTINCT Location FROM Practical.dept;
Select * FROM Practical.branch;
10. a) Create
view using single table with selected columns.
CREATE
VIEW Practical.newview AS SELECT Empname,Job From Practical.employee;
Select * FROM Practical.newview;
b) Create
view using multiple tables using selected columns.
CREATE
VIEW Practical.locview AS SELECT Empname, Job, Location FROM Practical.employee, Practical.dept WHERE
employee.Deptno=dept.Deptno;
Select
* FROM Practical.locview;
11. a) Delete
selected records from table by using some conditions.
Delete
FROM Practical.employee WHERE Salary between 25000 and 50000;
b) Drop column from
table.
ALTER TABLE
Practical.employee DROP COLUMN Phone_no;
c) Truncate
table.
Truncate
table Practical.employee;
d) Drop
table.
DROP
TABLE Practical.dept;
As
in Table employee deptno is defined as Foreign
Key, so we unable to delete it . To Delete it first we have to remove
table employee key constraint or delete table employe.
DROP
TABLE Practical.employee;
DROP
TABLE Practical.dept;
































No comments:
Post a Comment